Mastering Excel's User Interface: A Comprehensive Guide
Written on
Chapter 1: Understanding Excel's User Interface
Excel's interface has undergone significant transformations over the years. Familiarity with its layout is essential for leveraging the software effectively. From its initial iterations to the contemporary Ribbon layout, Excel has consistently enhanced user interaction with its functionalities. This article delves into the main elements of Excel's interface — specifically, the Ribbon, Tabs, and Menus — and how they collectively boost your productivity.
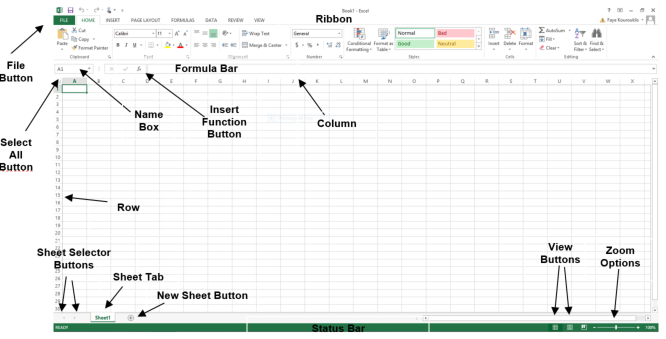
Section 1.1: The Ribbon - Your Command Center
The Ribbon, introduced in Excel 2007, revolutionized the user interface by replacing traditional menus and toolbars. It consolidates commands and features into an organized layout, simplifying the process of locating and utilizing Excel's vast capabilities.
Overview: Positioned at the top of the Excel window, the Ribbon is segmented into various tabs, each housing groups of related commands.
Tabs: Each tab on the Ribbon serves a unique function. For instance, the “Home” tab encompasses tools for formatting, alignment, and basic data operations, while the “Data” tab is dedicated to data management and analysis.
Groups: Commands within each tab are further organized into groups. In the “Home” tab, for example, the “Font” group includes options for font style and size, whereas the “Alignment” group handles text positioning.
Pro Tip: Personalize the Ribbon by adding or removing tabs and commands according to your workflow. To do this, right-click on the Ribbon and select “Customize the Ribbon.”
The first video, "Introduction to Microsoft Excel User Interface," provides a foundational understanding of Excel's layout and features.
Section 1.2: Tabs - Organizing Functionality
Tabs are an integral part of the Ribbon, designed to categorize Excel's commands logically:
- Home Tab: The default tab containing frequently used commands like font formatting and cell alignment.
- Insert Tab: This tab facilitates the insertion of various elements, such as charts, tables, and images into your worksheets.
- Page Layout Tab: Here, you'll find commands for modifying the appearance of your worksheet, including margins and themes.
- Formulas Tab: This tab offers tools for creating and managing formulas, including function libraries.
- Data Tab: Focused on data management, it includes features for sorting, filtering, and analyzing data.
- Review Tab: Provides tools for reviewing and editing your workbook, including spell check and comments.
- View Tab: Enables you to adjust your workbook's view settings, such as zoom levels and window arrangement.
Pro Tip: Use keyboard shortcuts for quick tab navigation. Pressing Alt activates Ribbon shortcuts for faster access to commands.
Conclusion
Grasping the components of Excel's interface — particularly the Ribbon, Tabs, and Menus — is essential for becoming a proficient user. By mastering these elements and customizing your workspace, you can streamline your workflow and harness Excel's powerful features to their fullest potential.